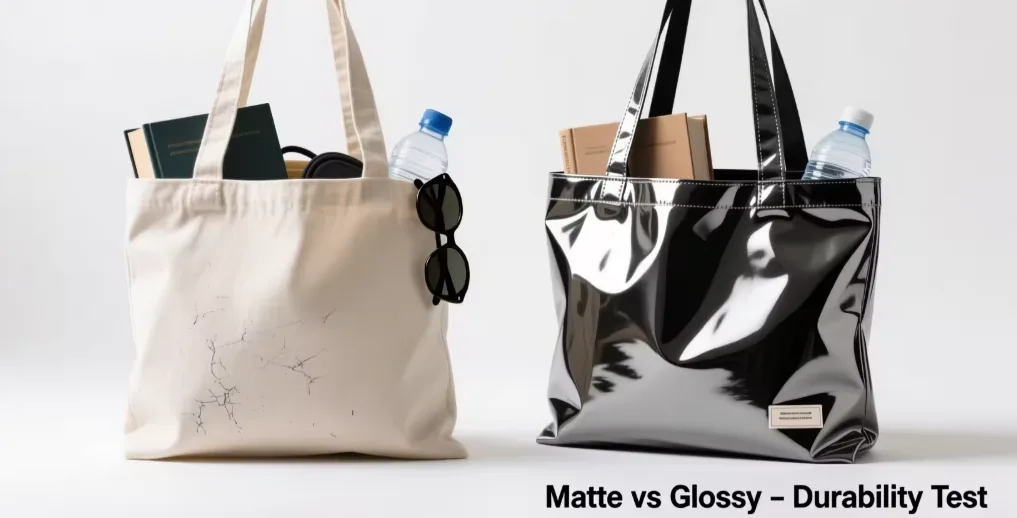
Some tote bags carry your laptop, gym gear, and groceries for years. Others fall apart in weeks.
What’s the difference? The answer hides in every stitch, seam, and fabric choice.
How a custom fashion tote works matters more than you think. Learn about hidden supports and smart materials. This knowledge turns you from a casual buyer into someone who spots quality fast. You’ll know what makes a tote worth the price.
Looking for a work bag or weekend carry-all? Structure, materials, and style work together. Get this right, and you stop buying bags that look good but fail fast.
This guide breaks down what makes totes perform well. You’ll see the construction tricks designers use. Plus, you’ll get styling tips that boost both durability and looks in your routine.
The Anatomy of a Fashion Tote: Core Structural Components
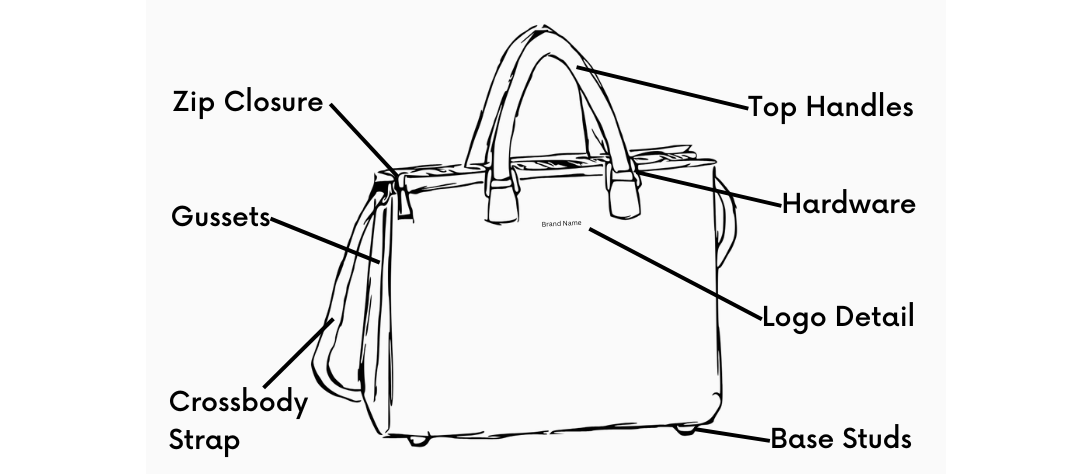
Every tote bag starts with five key parts. The main body, gussets, bottom panel, handles, and internal lining work as a system. These components show you how a fashion tote works under regular use.
Main Body Construction
The main body defines your tote’s primary storage space. Width measures across the opening—usually 38-50 cm (15-19.7″) for standard sizes. Height runs from bottom to top edge, not counting handles. Depth measures front-to-back thickness. This controls how much bulk fits inside.
Pattern makers use precise measurements for cutting fabric. Front and back panels measure 46.5 × 50 cm before putting them together. The opening might span 18″ × 10″ at the top. It tapers to 18″ × 8″ at the bottom. This taper creates a structured shape. The bag won’t sag.
Gusset Systems
Gussets turn flat fabric into three-dimensional storage. Box gussets use rectangular side and bottom panels. You get maximum stiffness. U-gussets require two seams. They offer moderate structure. T-gussets feature a single bottom seam. They add depth without side panels.
Small gusset changes alter capacity a lot. A 12 cm side gusset versus 15 cm changes volume from 15-20 liters to 25-30 liters. Wide, shallow gussets suit flat items like laptops. Deep gussets fit odd shapes better.
Bottom Panel Engineering
The bottom panel carries the entire load. Flat bottoms measure width by depth. These dimensions matter more than anything else for base capacity. Boat-style bottoms narrow at the base. Weight stays centered. This builds strength.
Structured totes often use firmer leather on lower panels. A quality leather tote might use 5.5-6 oz (2.2-2.5 mm) firm vegetable-tanned leather on the bottom. The upper sections get softer 5.5 oz (2.2 mm) material. This two-layer method balances strength with looks.
Handle Architecture
Strap measurements affect how comfortable the bag feels. Standard straps measure 6 × 80 cm each before attachment. Point-to-point measurement (sewn attachment to sewn attachment) sets the actual drop length. A 20-22″ total length creates a 9-11″ shoulder drop. Crossbody styles require 24-26″ for a 12-13″ drop.
Handle width and attachment strength must match bag size. Extra-large 35+ liter totes need stronger stitching. Thicker strap material stops tearing under heavy loads.
Reinforcement Systems: What Makes a Tote Durable

Strategic reinforcement at every stress point creates durability. How a fashion tote works under heavy loads depends on these hidden strength systems.
Handle Attachment Reinforcement
Handle connections face the most stress in any tote. Bar tacking adds extra strength where handles meet the bag body. This stops handles from pulling through. Triple stitching secures heavy loads with extra thread layers. Box pleating spreads stress across a wider area. No single point takes all the force.
Handle width affects comfort and durability. Wider handles spread pressure across your shoulder. This cuts strain on you and the attachment points. Double-stitched or riveted handles add strength that beats standard single-stitch methods.
Bottom Panel Protection
The bottom gets constant pressure and wear from surfaces. Flat bottom design provides stability. It spreads weight across the base. Box corners create a stable base structure. This stops sagging.
Bottom panels add an extra layer underneath. Edge binding protects bottom edges from scraping. You set the bag down, and these take the hit. Foot reinforcements lift the bag a bit from surfaces. This cuts direct wear. Some designs include drainage provisions. These stop moisture from building up inside.
Fabric Reinforcement Technology
Reinforcement patches appear at stress areas—corners, handle bases, and bottom edges. Laminated fabrics boost performance without adding bulk. Interface materials give structure between fabric layers.
Thermal bonding creates seamless reinforcement you can’t see from outside. This adds strength without extra stitching. Weight optimization means targeted strength where it’s needed. You get durability without extra weight.
Quality totes use layers in smart ways. A canvas tote might feature 250-350 GSM (medium-weight) fabric in low-stress areas. This offers 2-5 years lifespan with up to 15kg load capacity. Critical zones get 350-500 GSM (heavy-weight) material. This extends lifespan beyond 5 years with 25kg capacity.
Seam Strength Standards
Double-stitched or bound seams stop bags from splitting under heavy items. Strong seams prevent fraying at stress points. Reinforced stitching at handles and seams fights tearing under repeated loads.
Canvas quality affects durability. Thread count ranges from 250-400 threads per inch for standard weave. Heavy-duty canvas reaches 400-600 threads per inch. Weave density measures 20-30 threads per cm (standard) or 30-40 threads per cm (heavy-duty).
Long-staple cotton fibers (32-38mm) give better strength than medium-staple (25-32mm) or short-staple (less than 25mm) options. Tensile strength testing (ASTM D5034) checks that canvas meets minimum 150N requirements. This standard means the fabric can handle expected loads before breaking.
Material-Specific Durability
Full-grain leather totes last decades with proper care. They develop unique patina over years. High-density polyethylene (HDPE) offers strength and wear resistance for industrial jobs. Reinforced corners on structured totes give extra support for heavy parts.
Synthetic fabrics like nylon and polyester add water resistance. Polyester stays lightweight and water-resistant for regular use in wet conditions. These materials resist wear in ways natural fibers can’t. Modern design gives them similar life spans.
Making Totes Last Longer

Manufacturers test totes under real stress before you buy them. These tests show which products last and which ones break down fast.
Treating Hardware and Coatings
Metal parts need surface prep to fight rust. Chromate treatments give the best strength in all tests. This chemical process protects zippers, rivets, and snaps.
Phosphate surfaces come in second. They cost less than chromate. Plus, they boost metal life by 30-40% compared to untreated parts.
Degreased-only treatments offer the least protection. But they still beat raw metal.
Iron-zinc alloy coatings protect steel parts from the elements. Tests prove coated parts keep 60-70% more strength than uncoated ones. This holds true after a year of humid conditions.
Coastal climates and year-round outdoor use put totes to the test. These coatings make a real difference.
How Testing Works
Good leather bag manufacturers use variance analysis (ANOVA). This finds what affects how long a tote lasts. Three things matter most:
- Time under load: Long stress tests find weak spots
- Adhesive choice: Bad glue makes parts separate at stress points
- Protective coatings: Surface treatments add 40-60% more hardware life
Box plots and range tests compare different material batches. This spots bad quality early, before mass bag production starts. Look for manufacturers who share their quality data. You get better products this way.
Conclusion
Once you understand how tote bags are really made, you stop buying with your eyes and start buying with your brain.
From a factory’s very honest point of view: structure beats slogans. A strong base, smart strap attachment, and good material choice decide whether a tote lasts three months or three years.
Leather looks great but hates gym life. Canvas breathes but fears rain. Minimalist designs look cool until your phone meets your keys.
When you customize a tote bag, don’t ask “Is it trendy?”
Ask “Can it survive my lifestyle?”
The best tote isn’t the prettiest.
It’s the one that keeps up with you.






