Ever wondered why some custom leather backpacks last decades while others fall apart in months? The secret isn’t just in the leather itself. It’s in the smart engineering that transforms raw hide into a bag you can trust each day.
Understanding how a leather backpack works goes beyond its classic look. You’ll discover why certain designs spread weight across your shoulders without strain. You’ll see why specific stitching patterns stop complete failure. You’ll learn how the right hardware separates frustration from smooth function.
Investing in your first quality leather bag? Curious about the craft behind your current favorite? This complete guide breaks down every element. We cover the structure of the leather to the physics of weight spread. You get the knowledge to choose smart, maintain it right, and appreciate the mechanics hiding in plain sight.
Leather Backpack’s Weight Distribution and Carry Comfort

Backpack loads measured as percentage of body mass (BM) show key design differences. Studies test ranges from 0–70% BM to map how weight placement affects your spine and posture.
How Load Position Changes Your Body Mechanics

Modified double-pack designs place most weight on your back with minimal front load. Your spine stays closer to neutral alignment compared to single backpacks or evenly-split double packs.

Front-only packs force your body to lean backward. This compensates for forward weight pull. Your lower back arches under this stress in ways it shouldn’t.
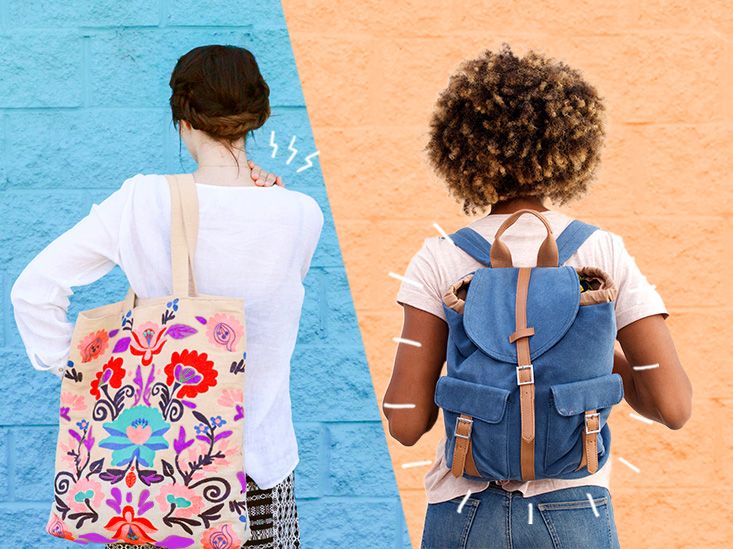

I learned this the hard way. For years, I carried a single-shoulder bag on my right side during daily commutes and factory visits. The load was never heavy enough to feel “dangerous,” but the constant imbalance forced my shoulder to elevate and my neck to tilt slightly for hours. Over time, this led to chronic shoulder inflammation and restricted movement—what doctors later diagnosed as shoulder periarthritis. The bag didn’t hurt in the moment. The damage came from repetition and poor load positioning.
Quality leather backpacks use these principles through strategic padding placement. The 5–10 mm foam layers mentioned earlier don’t just cushion. They distribute load across your body. Thicker padding sits at ischial contact points (where hip bones meet the belt). This mimics ergonomic chair design. Pressure spreads across a wider surface area. It doesn’t concentrate on bone protrusions.
Spinal Load Reduction Through Design
Manual lifting studies show proper weight distribution cuts spinal stress. Workers lifting 600 ml boxes faced 19,778 N compressive force at the L5/S1 vertebrae before ergonomic fixes.
After adjusting load height and position closer to body center mass, compression dropped to 3,350 N. Shear force fell from over 500 N to 185 N.
Backpack designers copy this by positioning heavy items close to your shoulder blades, centered between left and right sides. Internal laptop sleeves place that 2 kg weight against your back panel. Not hanging at the bottom where it creates a pendulum effect.
Compression straps pull shifting loads inward. This keeps the center of mass alignment that protects your L5/S1 joint during walking.
Adjustable strap systems let you customize this distribution. Tightening lower straps shifts more weight to hip belts (up to 60% transfer). Loosening them puts load across shoulders. Your torso length and load weight determine the optimal split.
Leather Backpack’s Compartments and Daily Organization

Pocket placement decides if you fumble for your phone or grab it fast. Smart compartment design sets professional leather backpacks apart from decorative ones that slow you down each day.
Laptop and Device Protection Zones

Laptop sleeves fit 13″–16″ screens with internal width 1–2 cm larger than your device. This extra space stops binding during insertion. Foam walls absorb shock. Premium models put the sleeve against your back panel—the most stable spot during movement. Your expensive electronics stay away from external impact points.
Tablet pockets measure 1–1.5 cm wider than protective cases. Depth extends 1–2 cm beyond case height. Soft fabric lining stops screen scratches. Devices shift during commutes. The lining protects them.
Quick-Access Exterior Pockets
Water bottle pockets feature circumference 2–3 cm larger than bottle diameter. Depth runs 60–75% of bottle height. Deep enough to secure the bottle. Shallow enough for single-hand retrieval without looking. Elastic panels fit different bottle sizes from 500–750 ml capacity.
On a normal workday morning, those front utility pockets quietly save time. When you’re approaching a subway gate with a bag on one shoulder, you don’t want to stop, set the bag down, and unzip the main compartment just to find a transit card. A front slip pocket lets your hand go straight in—card out in seconds, no looking, no fumbling.
The same applies to keys and sunglasses. Keys go into an open-access pocket instead of sinking to the bottom of the bag. Sunglasses slide into a dedicated front compartment with soft lining, so they don’t rub against metal or leather edges during daily movement. Over time, that padding isn’t a luxury detail—it’s what keeps lenses from getting micro-scratches caused by constant friction as you walk, turn, and commute.
In everyday use, these pockets aren’t about storage. They’re about reducing small interruptions that add up across a day.
Internal Organization Systems

Quality bags include 3–6 dedicated sections: phone slot, wallet compartment, pen loops, cable mesh pockets, and key clips. This multi-pocket setup cuts search time. Each item gets a fixed location.
Zippered wall pockets secure valuables—passports, credit cards, cash. Hidden compartments at bag’s bottom or side panels offer low-visibility storage. These use dead space. Theft targets stay out of sight.
Removable dividers convert layouts between work mode (laptop + documents) and travel mode (clothing stacks). This flexible system justifies premium pricing. You get real versatility.
Closure Engineering for Access Speed
Magnetic closures on workwear-inspired pockets enable one-hand opening. You can carry items in your other hand. Response time beats zippers by 2–3 seconds per access. This matters for catching buses or scanning building passes.
YKK metal zippers with reinforced tape handle 10,000+ open/close cycles without separation. Plastic hardware fails at temperature extremes. Leather bags face these extremes often.
External slip pockets balance security with speed for high-frequency items. Internal zippered sections protect low-frequency valuables. This layered approach matches closure type to how you use the bag. Not just zippers everywhere by default.
Leather Backpack’s Protection Against Rain and Weather

Leather gives you natural water resistance. But it’s not fully waterproof. The hide’s fiber structure pushes away light rain and splashes. Heavy or long exposure? That causes soak-through. This changes how you use the bag.
Water-Resistant vs Waterproof Performance
Water-resistant leather backpacks handle brief outdoor use. Think walking between buildings, light drizzle, or accidental spills. The leather surface makes water bead and roll off for 5–15 minutes. After that, moisture gets through the hide. Your stuff inside faces risk.
Waterproof leather backpacks use surface coatings that block water. These plastic-like films stop water entirely. But they change how the leather looks and feels. You lose natural texture. The bag breathes less. Summer heat makes it feel different against your back.
Leather Quality Sets Basic Protection
Full-grain and top-grain leather resist water better from the start. Dense fibers slow down moisture getting through. Genuine, bonded, and faux leather need chemical treatments right away. Wet conditions break down these materials fast without extra protection.
Load Capacity and Structural Durability for Backpack

Leather backpack testing uses methods from industrial load certification. Makers add controlled weight to check structural limits before products ship to buyers.
Static Load Testing Protocol
Quality backpacks go through static compression tests at 125–150% of advertised capacity. A 20 L bag rated for 10 kg gets tested with 12.5–15 kg loads. Tests run 24–48 hours to mimic long-term carrying stress. To pass, backpacks need zero strap detachment, no seam separation, and structural deformation under 5% of original size.
Premium brands test at multiple load levels. They test 50% rated load for 100,000 cycles (mimicking commutes). They test 100% rated load for 10,000 cycles (weekend trips). They test 150% rated load to find the failure point. This matches industrial durability standards. Industrial instruments handle 100,000 cycles at 50% capacity without accuracy drift.
Dynamic Movement Testing
Static weight shows part of the picture. Dynamic tests swing loaded bags through full range of motion. This includes shoulder shrugs, torso twists, and sitting-standing moves. Test machines repeat these movements 5,000–10,000 times at rated capacity. Strap anchor points face the most stress. Pulling forces spike to 2–3× static load during sudden stops or direction changes.
Bottom panel impact tests drop loaded bags from 0.5–1 meter heights onto concrete. Pass criteria: no hardware detachment, intact stitching, and functional zippers after 50 drops. This mimics years of setting bags down on floors and tossing them into vehicles.
Conclusion
How a leather backpack works goes beyond just carrying your stuff. Full-grain versus top-grain leather matters. Weight distribution systems matter. Every part affects performance, durability, and that patina that builds up over years.
Here’s what makes it work: premium leather gives you natural weatherproofing and breathability. Strong stitching holds up under heavy loads. Well-designed compartments keep your gear organized and easy to grab. Handcrafted or backpack mass-produced, these basics stay the same.
You’ve learned the complete mechanics. Time to use this knowledge. Check the stitching quality. Test the hardware. Feel the leather grain. See how the weight distribution fits your needs. A well-made leather backpack isn’t just an accessory. It’s a tool that gets better with age. Each trip makes it more yours.
Your backpack’s story starts the moment you know what makes it work.